Lab Grown Diamonds
Lab-grown diamonds require no mining, are as high-quality as mined diamonds, and offer superior value for their price.

Help us guide you in your journey
In life's defining moment, where love takes flight,
Trust our guidance to choose a ring that shines bright.
Let us weave enchantment, a symbol so pure,
The perfect ring for her, forever to endure.
Love at first sight
Every engagement is a special bond between two unique individuals. Just as each relationship is distinct, so should be the ring that symbolizes your love. Tailor the design to match the taste and personality of your loved one, ensuring a cherished token that reflects their individuality and your deep connection.
Create a cherished token that captures the essence of your deep connection, making them fall in love all over again. Visit us now!



Learn about
THE 4C'S OF DIAMONDS
The 4Cs of diamonds refer to the four essential characteristics used to assess and evaluate the quality and value of a diamond.
By considering these four factors, carat weight, color, clarity, and cut, diamond buyers and sellers can make informed decisions and understand the unique characteristics and value of a diamond.
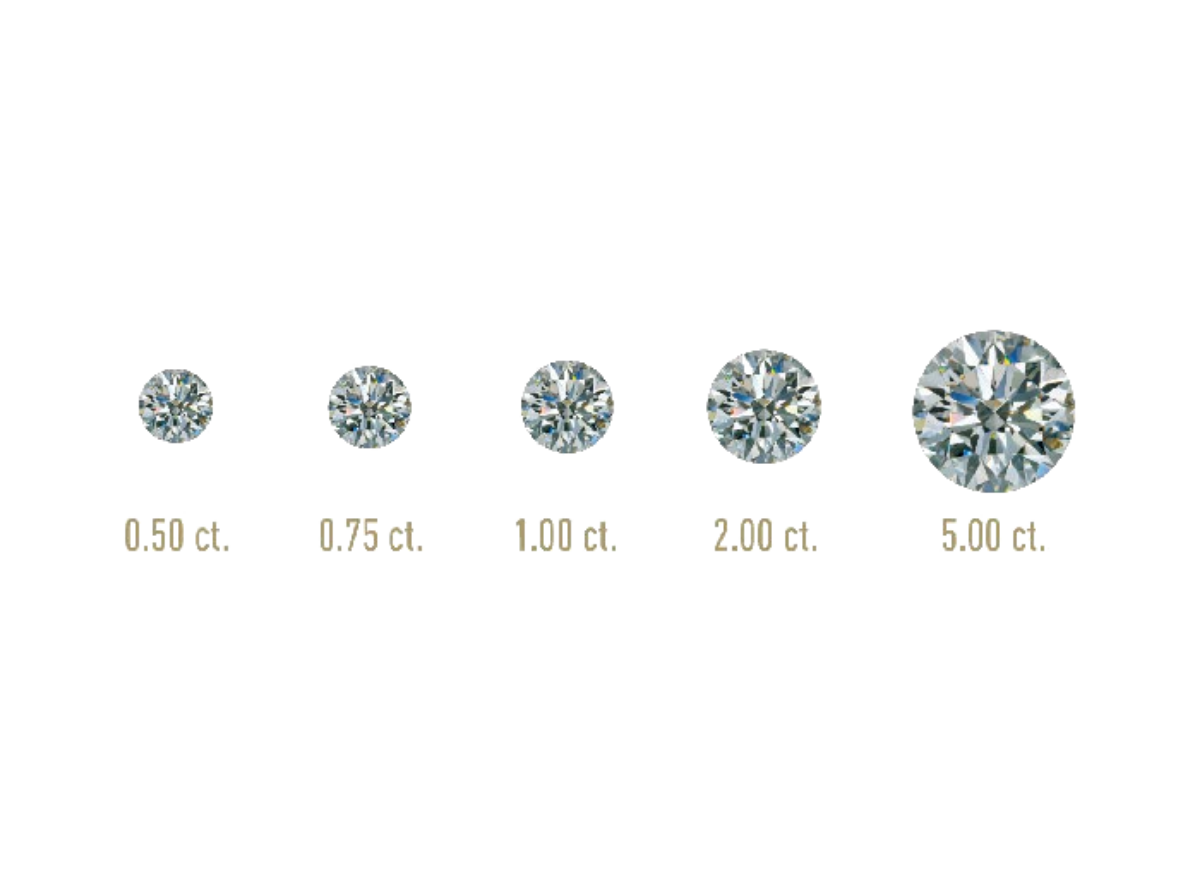
Carat Weight
A carat is a standard unit of measurement used to determine the weight of a diamond. Specifically, one carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams. Carat weight is commonly expressed in points, where one carat is made up of 100 points. For instance, a diamond weighing .50 carats can also be referred to as 50 points or 1/2 carat.While carat weight is a significant factor in determining the value of a diamond, it is important to note that the quality ratings of a diamond can greatly influence its worth, even if two diamonds have the same carat weight. Diamonds with higher or lower quality ratings may be valued significantly higher or lower, respectively, than their counterparts with equal carat weight.
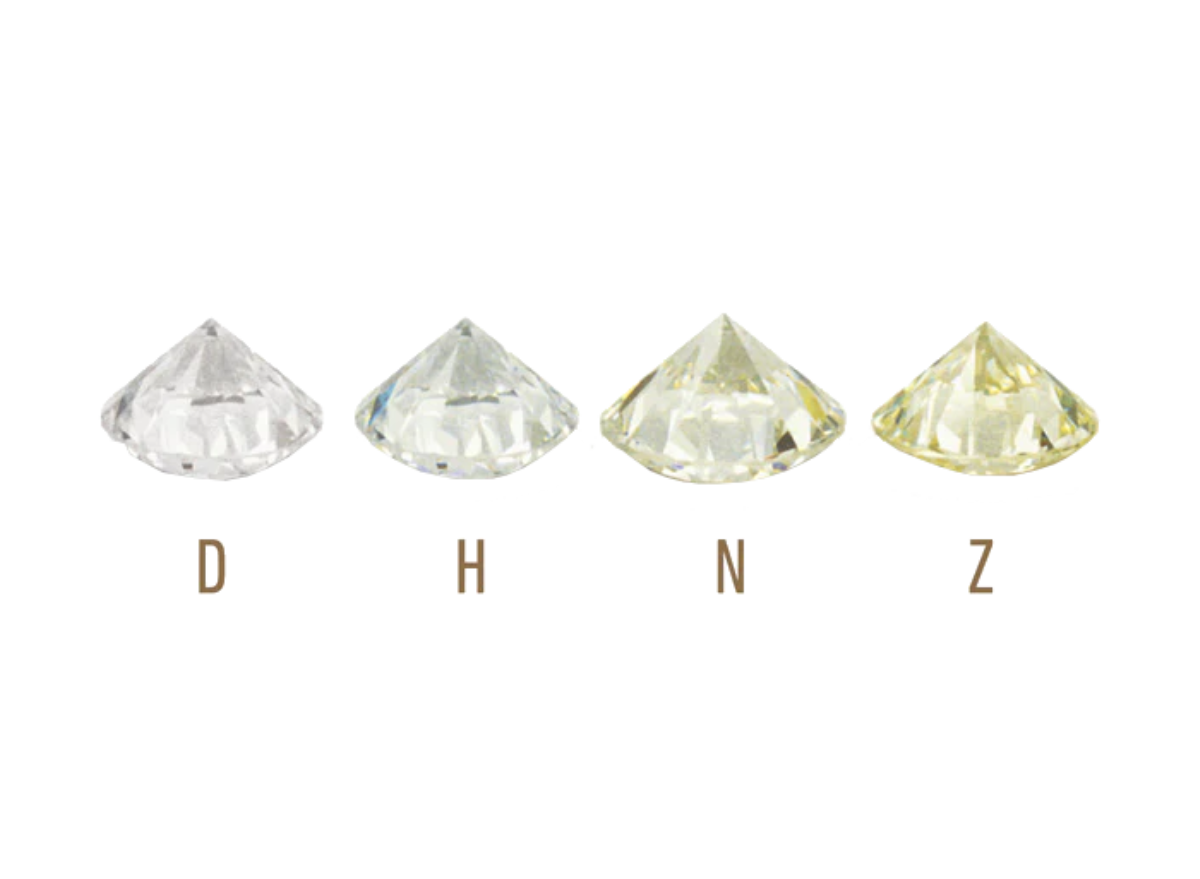

Colour
Diamonds exhibit a diverse range of colors, and their rarity significantly influences their value. The industry employs an alphabetical scale, starting from the letter D, to rate a diamond's color. D represents the whitest and purest color achievable in a diamond, often referred to as pure white. Naturally, diamonds rated closer to the top of this scale are appraised at a higher value, while those with a yellow tint are considered less valuable.It is worth noting that fancy color diamonds, which encompass hues like blue, green, and vibrant yellow, are exceptionally rare and come with a hefty price tag. These diamonds are particularly sought after and valued for their unique colors, making them even more precious.
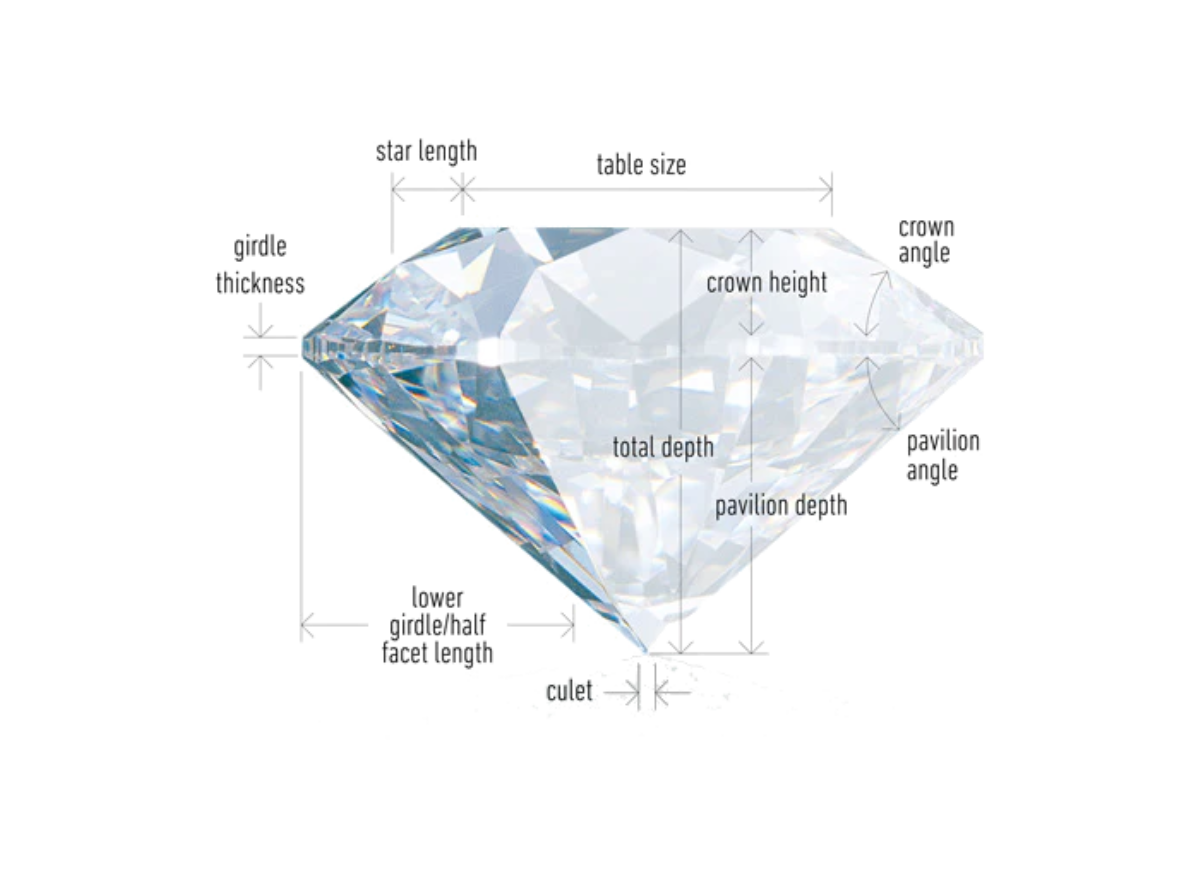
Cut
Contrary to common belief, a diamond's cut does not pertain to its shape. Instead, a diamond's cut refers to its depth, width, and the consistency of its facets. The brilliance of a diamond is greatly influenced by the quality of its cut.A well-cut diamond has the ability to showcase the vibrant colors that lie deep within the stone. It achieves this by maximizing the amount of light that enters through the table and reflects it back to the viewer through the same table. In contrast, a poorly cut diamond absorbs light through its table and emits it through the sides, rather than reflecting it back through the top. This reduced level of reflected light significantly impacts the diamond's sparkle and fire, resulting in diminished brilliance.
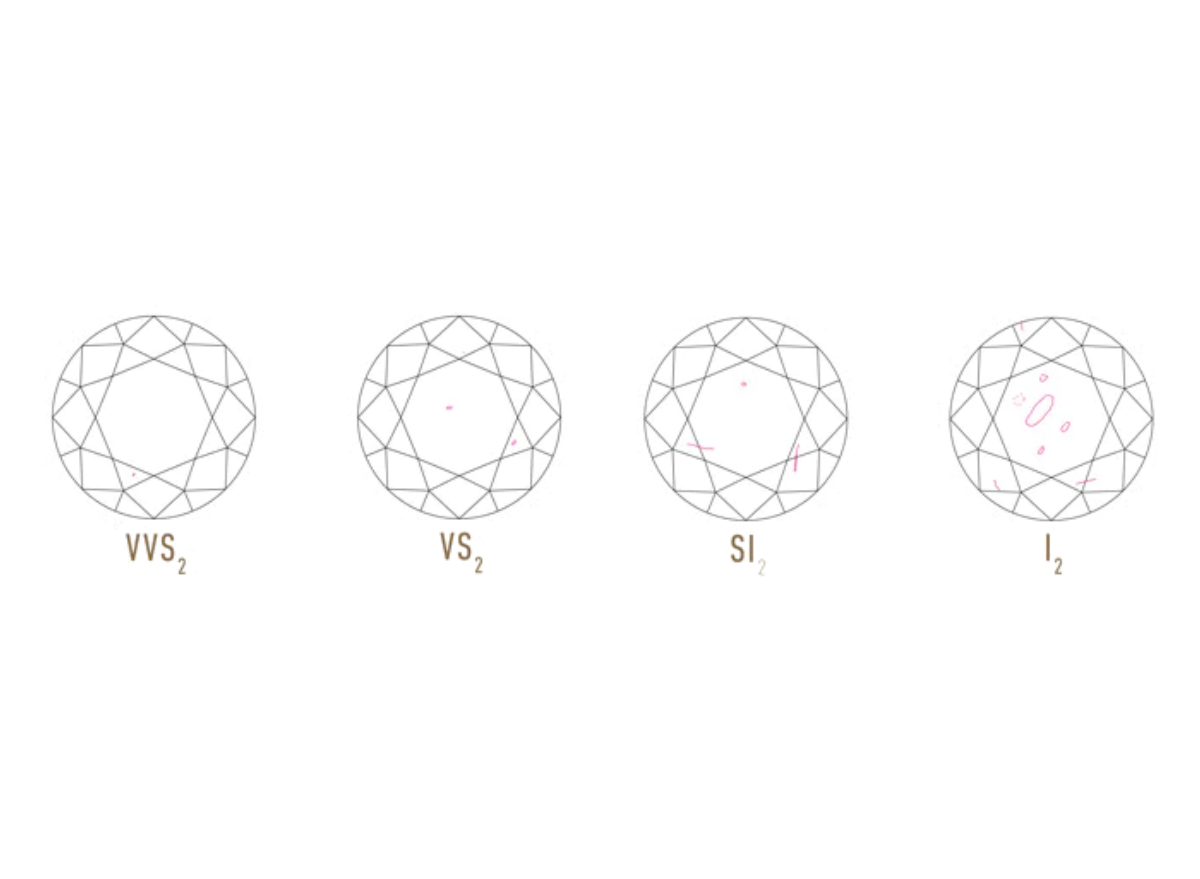
Clarity
Diamond clarity is determined by evaluating internal characteristics known as inclusions and external characteristics known as blemishes. These features result from the formation of diamonds under intense heat and pressure. The clarity of a diamond is assessed based on factors such as the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as their impact on the diamond's overall appearance.
While no diamond can achieve absolute purity, the closer it comes to being flawless, the higher its clarity.
Learn more on gia.edu


